The following which I pieced together, describes a possible connection between the sunspot/solar activity cycle and climate.
If you look at the chart below, you will see that sunspot activity (during solar maxes--the individual peaks every apprx 11 yrs) has been relatively high since about 1900 and almost non-existent for the period between about 1625 and 1725. This period is known as the Maunder (sunspot) Minimum or "Little Ice Age".-etl

____________________________________________________
From BBC News [yr: 2004]:
"A new [2004] analysis shows that the Sun is more active now than it has been at anytime in the previous 1,000 years. Scientists based at the Institute for Astronomy in Zurich used ice cores from Greenland to construct a picture of our star's activity in the past. They say that over the last century the number of sunspots rose at the same time that the Earth's climate became steadily warmer."..."In particular, it has been noted that between about 1645 and 1715, few sunspots were seen on the Sun's surface.
This period is called the Maunder Minimum after the English astronomer who studied it. It coincided with a spell of prolonged cold weather often referred to as the "Little Ice Age". Solar scientists strongly suspect there is a link between the two events - but the exact mechanism remains elusive."
http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/sci/tech/3869753.stm
____________________________________________________
It's really hard to imagine how this little ball of fire could have any impact on our climate at all. /s
But the main arguments being made for a solar-climate connection is not so much to do with the heat of the Sun (the sun isn't necessarily getting warmer) but rather with its magnetic cycles. When the Sun is more magnetically active (typically around the peak of the 11-year sunspot cycle --we are a few yrs away at the moment), the Sun's magnetic field is better able to deflect away incoming galactic cosmic rays (highly energetic charged particles coming from outside the solar system). The GCRs are thought to help in the formation of low-level cumulus clouds -the type of clouds that BLOCK sunlight and help cool the Earth. So when the Sun's MF is acting up (not like now -the next sunspot max is expected in about 2013, according to the latest predictions), less GCRs reach the Earth's atmosphere, less low level, sunlight-blocking clouds form, and more sunlight gets through to warm the Earth's surface...naturally. Clouds are basically made up of tiny water droplets. When minute particles in the atmosphere become ionized by incoming GCRs they become very 'attractive' to water molecules, in a purely chemical sense of the word. The process by which the Sun's increased magnetic field deflects incoming cosmic rays is very similar to the way magnetic fields steer electrons in a cathode ray tube (old-time television tube) or electrons and other charged particles around the ring of a subatomic particle accelerator.-etl
____________________________________________________
From 2008...
The Center for Sun-Climate Research at the DNSC (Danish National Space Center) investigates the connection between variations in the intensity of cosmic rays and climatic changes on Earth. This field of research has been given the name 'cosmoclimatology'"..."Cosmic ray intensities – and therefore cloudiness – keep changing because the Sun's magnetic field varies in its ability to repel cosmic rays coming from the Galaxy, before they can reach the Earth." :
http://www.spacecenter.dk/research/sun-climate
____________________________________________________
From a well-referenced wikipedia.com column (see wiki link for ref 14):
"Sunspot numbersover the past 11,400 years have been reconstructed using dendrochronologically dated radiocarbon concentrations. The level of solar activity during the past 70 years is exceptional — the last period of similar magnitude occurred over 8,000 years ago. The Sun was at a similarly high level of magnetic activity for only ~10% of the past 11,400 years, and almost all of the earlier high-activity periods were shorter than the present episode.[14]"
[14] ^Solanki, Sami K.; Usoskin, Ilya G.; Kromer, Bernd; Schüssler, Manfred & Beer, Jürg (2004), “Unusual activity of the Sun during recent decades compared to the previous 11,000 years”, Nature 431: 1084–1087, doi:10.1038/nature02995, . Retrieved on 17 April 2007 , "11,000 Year Sunspot Number Reconstruction". Global Change Master Directory. Retrieved on 2005-03-11.
____________________________________________________
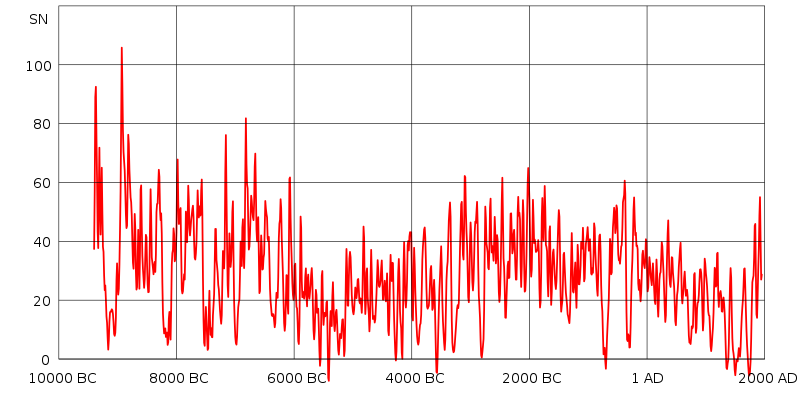
"Reconstruction of solar activity over 11,400 years. Period of equally high activity over 8,000 years ago marked.
Present period is on [the right]. Values since 1900 not shown."
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solar_variation
____________________________________________________
From NASA's Solar and Heliospheric Observatory's "Not So Frequently Asked Questions" section:
Q-Does the number of sunspots have any effect on the climate here on Earth?
A-Sunspots are slightly cooler areas on the surface of the Sun, due to the intense magnetic fields, so they radiate a little less energy than the surroundings. However, there are usually nearby areas associated with the sunspots that are a little hotter (called falculae), and they more than compensate. The result is that there is a little bit more radiation coming from the Sun when it has more sunspots, but the effect is so small that it has very little impact on the weather and climate on Earth.
However, there are more important indirect effects: sunspots are associated with what we call "active regions", with large magnetic structures containing very hot material (being held in place by the magnetism). This causes more ultraviolet (or UV) radiation (the rays that give you a suntan or sunburn), and extreme ultraviolet radiation (EUV). These types of radiation have an impact on the chemistry of the upper atmosphere (e.g. producing ozone). Since some of these products act as greenhouse gases, the number of sunspots (through association with active regions) may influence the climate in this way.
Many active regions produce giant outflows of material that are called Coronal Mass Ejections. These ejections drag with them some of the more intense magnetic fields that are found in the active regions. The magnetic fields act as a shield for high-energy particles coming from various sources in our galaxy (outside the solar system). These "cosmic rays" (CRs) cause ionization of molecules in the atmosphere, and thereby can cause clouds to form (because the ionized molecules or dust particle can act as "seeds" for drop formation).
If clouds are formed very high in the atmosphere, the net result is a heating of the Earth - it acts as a "blanket" that keeps warmth in.
If clouds are formed lower down in the atmosphere, they reflect sunlight better than they keep heat inside, so the net result is cooling. Which processes are dominant is still a matter of research.
http://sohowww.nascom.nasa.gov/classroom/notsofaq.html#SUNSPOT_CLIMATE
____________________________________________________
NASA graph of sunspot activity over the past 400 years [note the profound lack of sunspot activity during the "Little Ice Age" period (apprx 1650-1720), AND the sharp INCREASE particularly during the past 60 years:

http://science.nasa.gov/ssl/pad/solar/images/ssn_yearly.jpg
____________________________________________________

100,000-Year Climate Pattern Linked To Sun's Magnetic Cycles:
ScienceDaily (Jun. 7, 2002) HANOVER, N.H.
Thanks to new calculations by a Dartmouth geochemist, scientists are now looking at the earth's climate history in a new light. Mukul Sharma, Assistant Professor of Earth Sciences at Dartmouth, examined existing sets of geophysical data and noticed something remarkable: the sun's magnetic activity is varying in 100,000-year cycles, a much longer time span than previously thought, and this solar activity, in turn, may likely cause the 100,000-year climate cycles on earth. This research helps scientists understand past climate trends and prepare for future ones.
http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2002/06/020607073439.htm