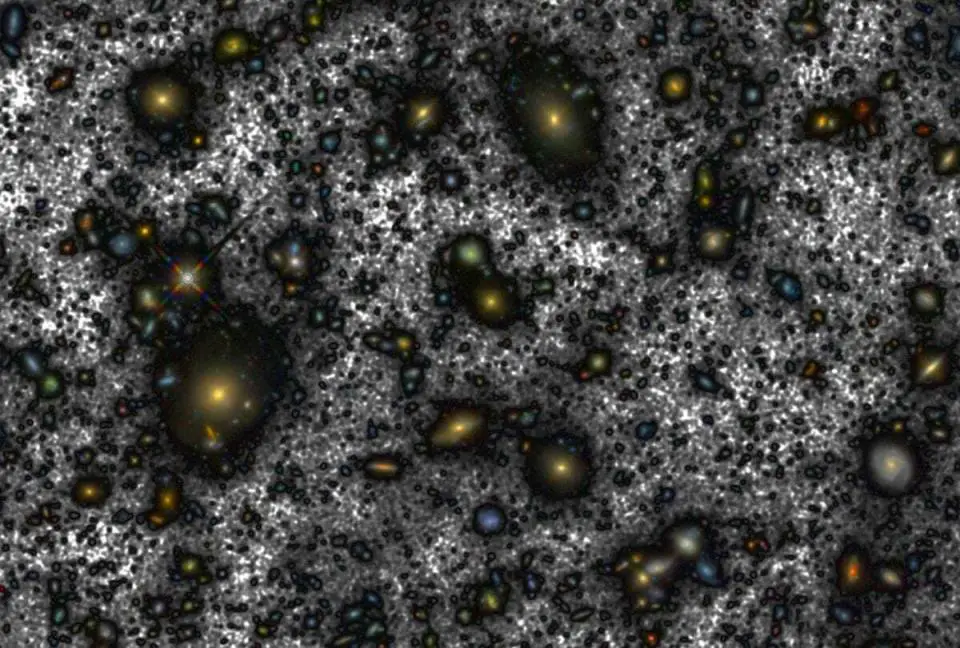
Credit: Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias

Basically, 2,000+ galaxies were revealed in a speck of sky which could be blocked out by a grain of sand held at arm's length!
_______________________________________
January 15, 1996

Several hundred never before seen galaxies are visible in this “deepest-ever” view of the universe, called the Hubble Deep Field (HDF), made with NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope.
Besides the classical spiral and elliptical shaped galaxies, there is a bewildering variety of other galaxy shapes and colors that are important clues to understanding the evolution of the universe. Some of the galaxies may have formed less that one billion years after the Big Bang.
Representing a narrow “keyhole” view all the way to the visible horizon of the universe, the HDF image covers a speck of sky 1/30th the diameter of the full Moon (about 25% of the entire HDF is shown here).
This is so narrow, just a few foreground stars in our Milky Way galaxy are visible and are vastly outnumbered by the menagerie of far more distant galaxies, some nearly as faint as 30th magnitude, or nearly four billion times fainter than the limits of human vision. (The relatively bright object with diffraction spikes just left of center may be a 20th magnitude star.)
Though the field is a very small sample of sky area it is considered representative of the typical distribution of galaxies in space because the universe, statistically, looks the same in all directions.
The image was assembled from many separate exposures (342 frames total were taken, 276 have been fully processed to date and used for this picture) with the Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2), for ten consecutive days between December 18 to 28, 1995. This picture is from one of three wide-field CCD (Charged Coupled Device) detectors on the WFPC2.
This “true-color” view was assembled from separate images were taken in blue, red, and infrared light. By combining these separate images into a single color picture, astronomers will be able to infer—at least statistically—the distance, age, and composition of galaxies in the field. Bluer objects contain young stars and/or are relatively close, while redder objects contain older stellar populations and/or farther away.
https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/spaceimages/details.php?id=PIA12110
One of the main scientific justifications for building Hubble was to measure the size and age of the Universe and test theories about its origin. Images of faint galaxies give 'fossil' clues as to how the Universe looked in the remote past and how it may have evolved with time. The Deep Fields gave astronomers the first really clear look back to the time when galaxies were forming. The first deep fields – Hubble Deep Field North and South – gave astronomers a peephole to the ancient Universe for the first time, and caused a real revolution in modern astronomy.
Subsequent deep imagery from Hubble, including the Hubble Ultra Deep Field, has revealed the most distant galaxies ever observed. Because of the time it has taken their light to reach us, we see some of these galaxies as they were just half a billion years after the Big Bang.
Deep field observations are long-lasting observations of a particular region of the sky intended to reveal faint objects by collecting the light from them for an appropriately long time. The 'deeper' the observation is (i.e. longer exposure time), the fainter are the objects that become visible on the images. Astronomical objects can either look faint because their natural brightness is low, or because of their distance. In the case of the Hubble Deep and Ultra Deep Fields, it is the extreme distances involved which make them faint, and hence make observations challenging.
Using the different Hubble Deep fields astronomers were able to study young galaxies in the early Universe and the most distant primeval galaxies. The different deep fields are also a good gathering grounds to find the most distant objects ever observed.
The idea for the Hubble Deep Fields originated in results from the first deep images taken after the repair in 1993. These images showed many galaxies, which were often quite unlike those we see in the local Universe and could not otherwise be studied using conventional ground-based telescopes. The first Deep Field, the Hubble Deep Field North (HDF-N), was observed over 10 consecutive days during Christmas 1995. The resulting image consisted of 342 separate exposures, with a total exposure time of more than 100 hours, compared with typical Hubble exposures of a few hours. The observed region of sky in Ursa Major was carefully selected to be as empty as possible so that Hubble would look far beyond the stars of our own Milky Way and out past nearby galaxies.
The results were astonishing! Almost 3000 galaxies were seen in the image. Scientists analysed the image statistically and found that the HDF had seen back to the very young Universe where the bulk of the galaxies had not, as yet, had time to form stars. Or, as the popular press dramatically reported, “Hubble sees back to Big Bang”. These very remote galaxies also seemed to be smaller and more irregular than those nearer to us. This was taken as a clear indication that galaxies form by gravitational coalescence of smaller parts.
In 1996 it was decided to observe a second Deep Field, the Hubble Deep Field South (HDF-S), to assess whether the HDF-N was indeed a special area and thus not representative of the Universe as a whole. This time the field also contained a quasar, which was used as a cosmological lighthouse and provided valuable information about the matter between the quasar and the Earth.
| |
"In my view the Hubble Deep Fields are some of the images that have made the greatest impact on observational cosmology so far. These impressive dips into the depths of space and time have allowed astronomers to glimpse the first steps of galaxy formation more than 10 billion years ago and are without doubt some of the great legacies of the Hubble Space Telescope."
|
|
After the Hubble observations of HDF-N and -S, other ground and space-based instruments targeted the same patches of sky for long periods. Some of the most interesting results seem to emerge from these fruitful synergies between instruments of different sizes, in different environments and with sensitivity to different wavelengths.
The Hubble Ultra Deep Field from 2004 represents the deepest portrait of the visible universe ever achieved by humankind. Using the improved capabilities of the Advanced Camera for Surveys, the camera installed during the 2002 servicing mission, a new Deep Field was observed, in the constellation of Fornax (the Furnace).
It reveals some of the first galaxies to emerge from the "dark ages", the time shortly after the Big Bang when the first stars reheated the cold, dim universe.
The Ultra Deep Fields show the furthest away galaxies that can be observed in visible light.
Because the Universe expands, light waves from very distant objects is stretched during its long journey to us. The further away objects are from us, the more their light is stretched. As longer wavelengths appear redder than shorter wavelengths, this phenomenon is known as “redshift”, and it is somewhat similar to the Doppler effect heard when an ambulance siren drops in pitch as the vehicle speeds away.
For very distant objects, their light is shifted so far that they drop out of the visible spectrum altogether, and can only be seen in infrared light. This means that the Hubble Ultra Deep Field cannot be improved on by building a more sensitive optical telescope — Hubble has reached the limit of what is possible in visible light.

Original
thanks
I hope the Webb telescope gets a chance to try the same thing.
What always boggles my mind with these is that - that’s only what’s in the direction the telescope was pointed. Granted it’s supposed to be toward the center, but think of all the stuff left out in the other 359* of view on 2 different planes.
Ah the arrogance. As if they had a clue as to when the beginning of time was.
(and it's one helluva lotta H, etc)
I am so screwed
Very interesting -- BUT --that is not the HUDF, it is a portion of the HXDF (Hubble Extreme Deep Field) image that they processed.
I don't know what stunt this article is trying to pull -- but, that's definitely the
Hubble Extreme Deep Field Image at https://apod.nasa.gov/apod/image/1210/xdf_hubble_960.jpg...
~~~~~~~~~~~~
It took a bit of "processing and tweaking" (including a bit of rotation) to obtain registration, but here's the AOI/ROI of the HXDF that Canarias reported on:
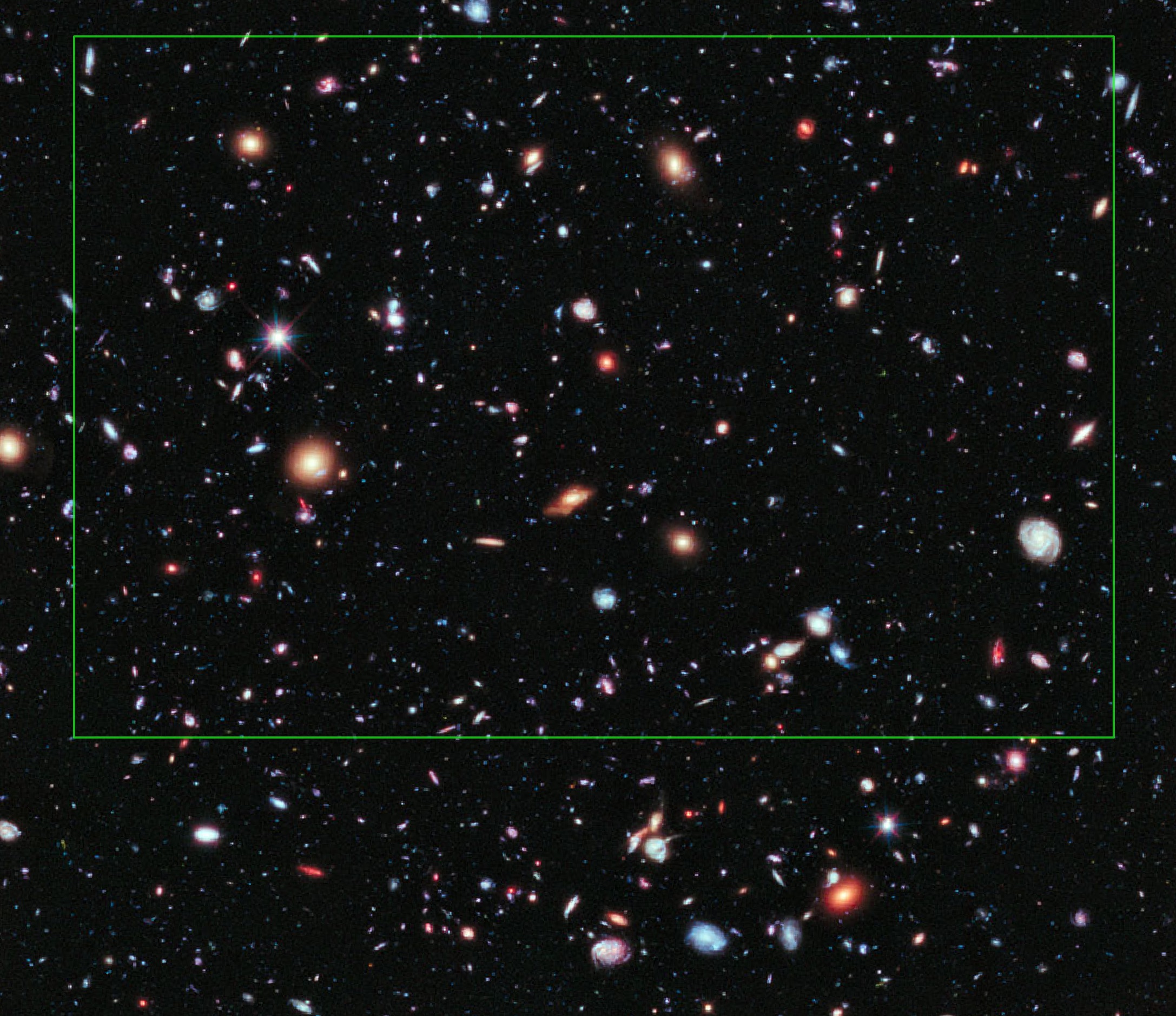

And, here's the Canarias image, superimposed on the XDF:
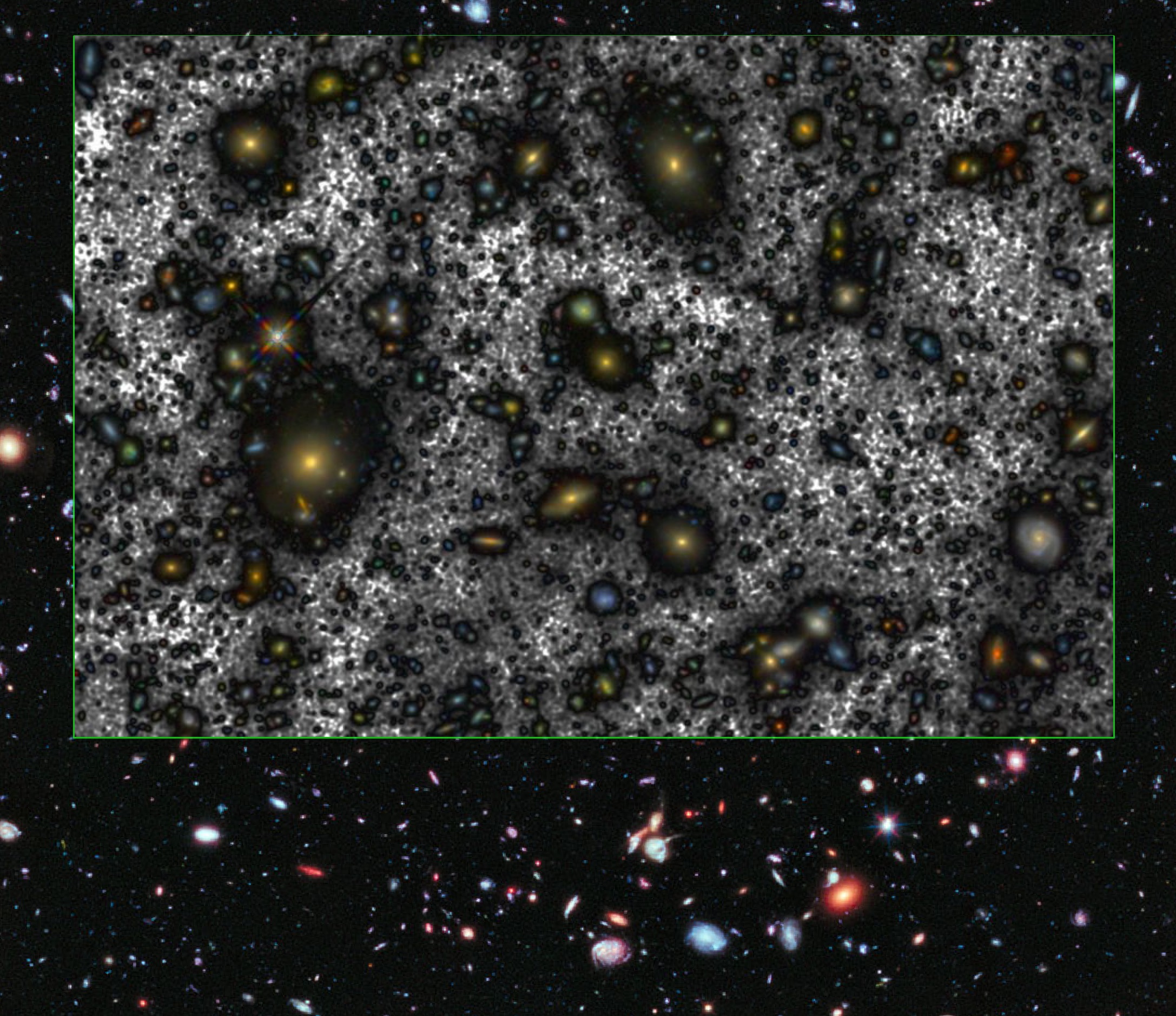

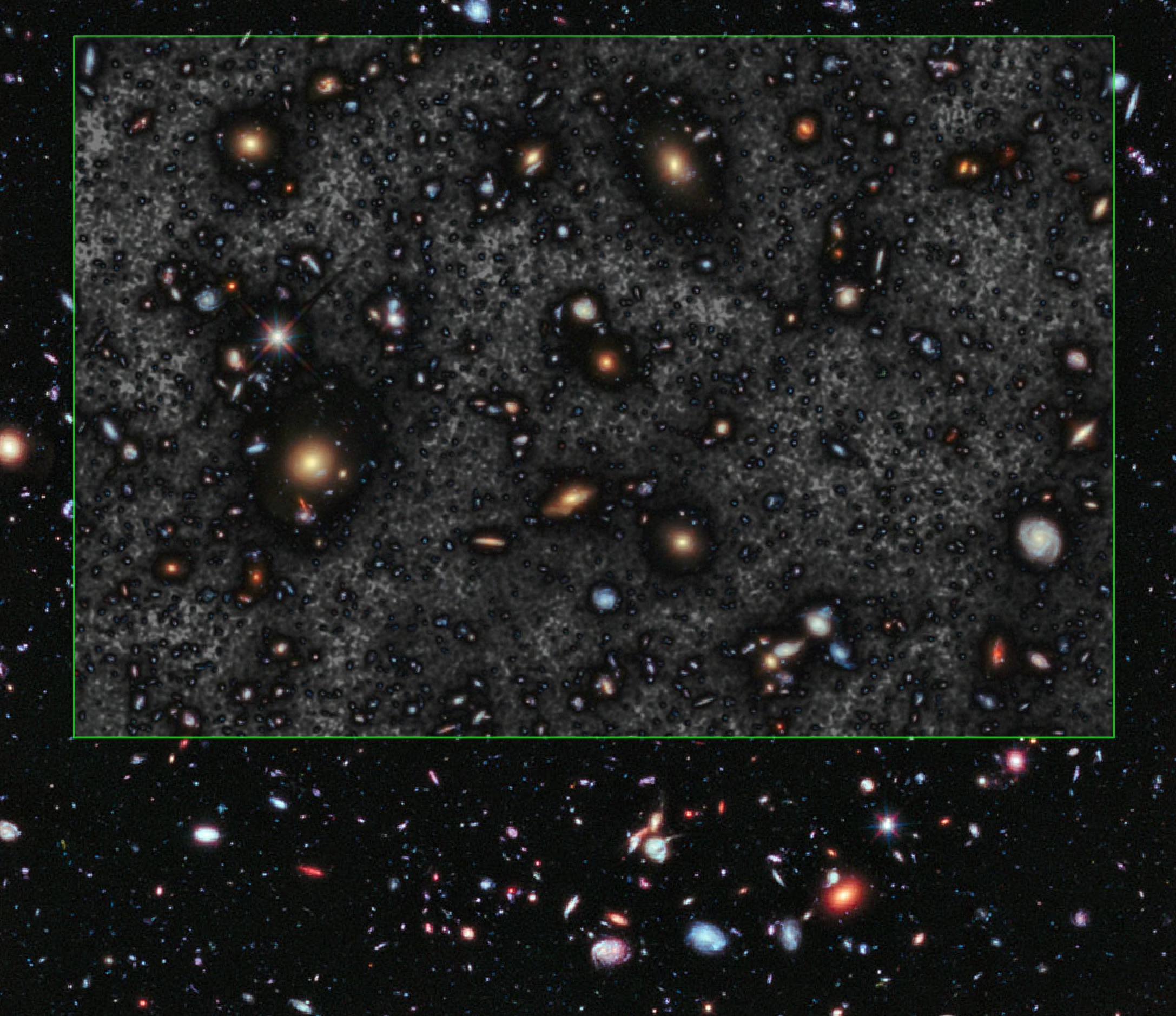
And, even more convincing, Canarias at 45% opacity:

And, the pièce de résistance, Canarias subtracted from XDF -- leaving mostly Canarias' "intra-galactic 'imaging artifacts'" visible:
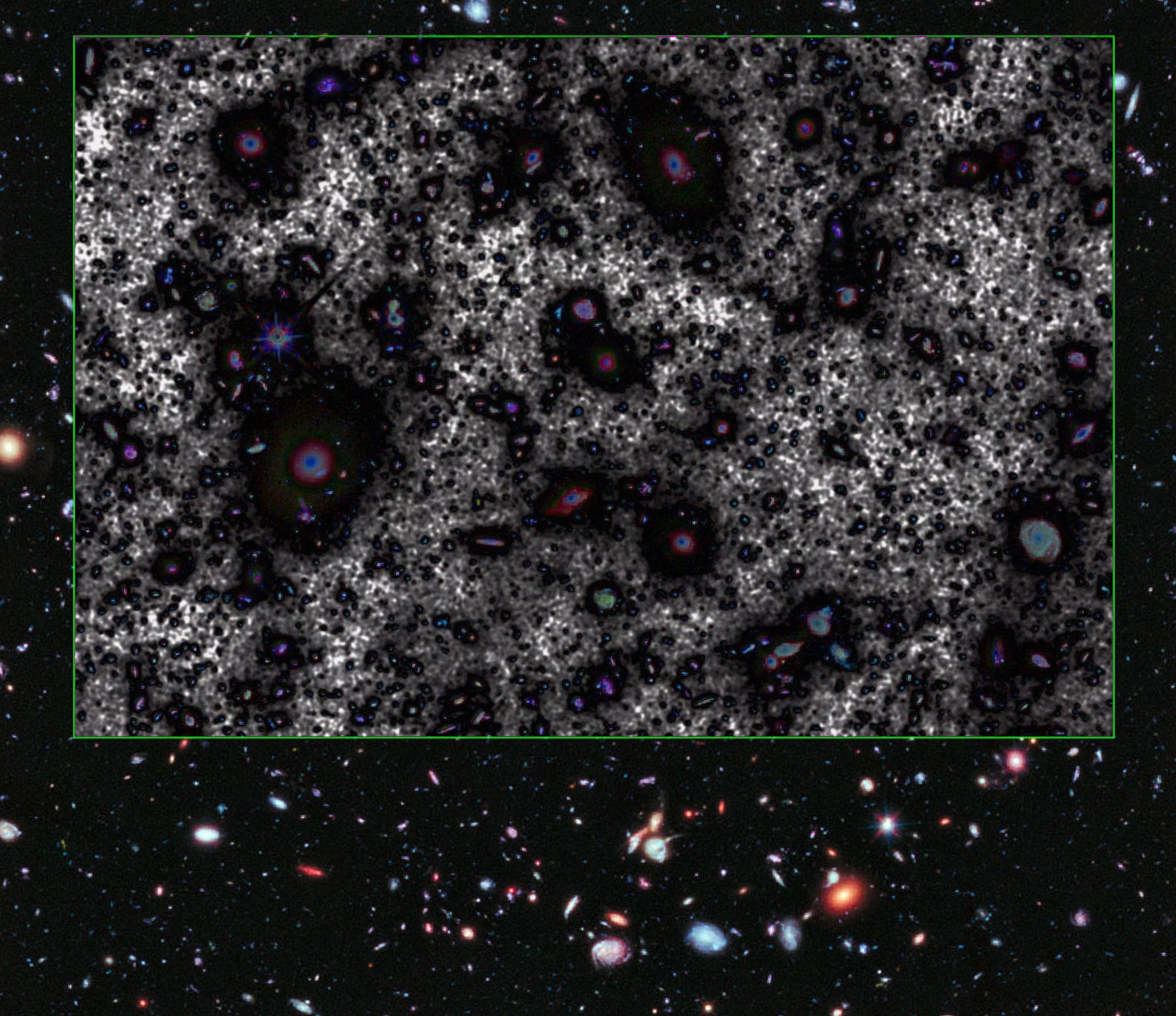

Seriously, I find reporting of the wrong base image to be deplorable -- but, I admit that those Canarias "imaging artifacts" (if they reflect actual objects/phenomena) may be their biggest contribution...
YMMV... '-)
TXnMA
