
Posted on 03/30/2022 8:24:51 PM PDT by LibWhacker

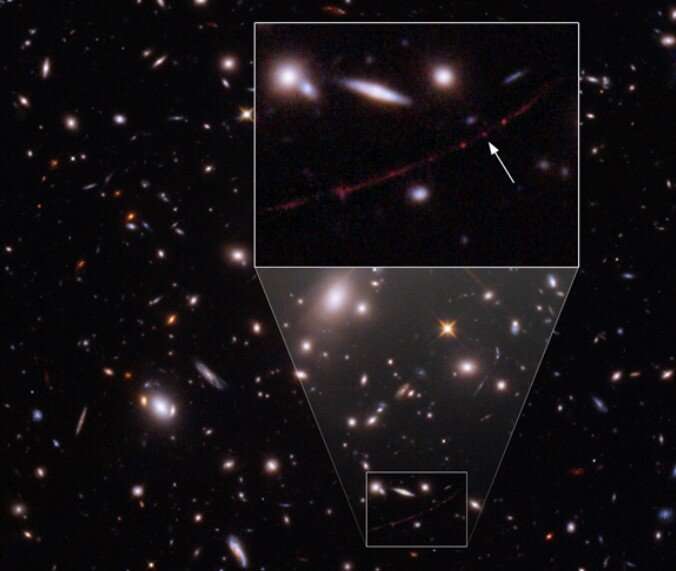
Closeup of the region on the sky, 1/250 of a degree across, where the gravity of a foreground cluster of galaxies magnifies the distant background star—nicknamed Earendil—thousands of times.
With a fortuitous lineup of a massive cluster of galaxies, astronomers discovered a single star across most of the entire observable Universe. This is the farthest detection of a single star ever. The star may be up to 500 times more massive than the Sun. The discovery has been published today in the journal Nature.
Gazing at the night sky, all the stars that you see lie within our own galaxy, the Milky Way. Even with the most powerful telescopes, under normal circumstances individual stars can only be resolved in our most nearby galactic neighbors. In general, distant galaxies are seen as the blended light from billions of stars.
But with the marvelous natural phenomenon known as "gravitational lensing," astronomers from the Cosmic Dawn Center at the Niels Bohr Institute and DTU Space were nevertheless able to detect a distance where even detecting entire galaxies is challenging.
A cosmic telescope predicted by Einstein
Among the wonders predicted by Einstein's theory of relativity is the ability of mass to "curve" space itself. As light passes close to massive objects, its path follows the curved space and changes direction. If a massive object happens to lie between us and a distant background source of light, the object may deflect and focus the light toward us as a lens, magnifying the intensity.
Galaxies magnified several times are routinely discovered by way of this method. But in an astounding cosmic coincidence, the galaxies in a cluster named WHL0137-08 happened to line up in such a way as to focus the light of a single star toward us, magnifying its light thousands of times.
A combination of this gravitational lens and nine hours of exposure time with the Hubble Space Telescope enabled an international team of astronomers to detect the star.
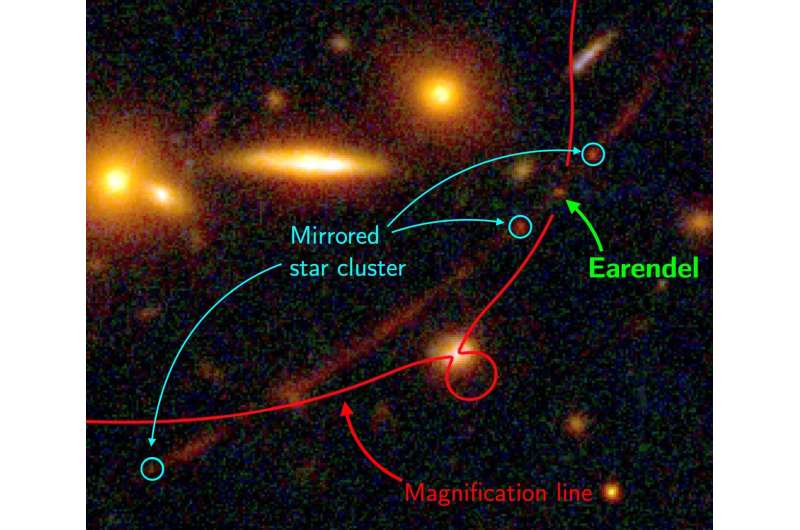
Close-up of the tiny region where Earendel happened to fall right on top of the narrow line where the magnification increases by (tens of) thousands of times. A cluster of many stars is seen slightly offset from the line, resulting in a much smaller magnification but instead being mirrored by gravity.
Earendel—the morning star
The astronomers nicknamed the star Earendel, from the Old English word meaning "morning star," or "rising light." They calculate that the star it at least 50 times as massive as our Sun, possibly up to 500, and millions of times as bright.
Besides being an astonishing achievement in itself, the observation of Earendel offers a unique possibility of investigating the early Universe:
"As we peer into the cosmos, we also look back in time, so these extreme high-resolution observations allow us to understand the building blocks of some of the very first galaxies," explains Victoria Strait, postdoc at the Cosmic Dawn Center, Copenhagen, and a collaborator and co-author of the study. She elaborates:
"When the light that we see from Earendel was emitted, the Universe was less than a billion years old; only 6% of its current age. At that time it was 4 billion lightyears away from the proto-Milky Way, but during the almost 13 billion years it took the light to reach us, the Universe has expanded so that it is now a staggering 28 billion lightyears away."
The previous record is a star seen when the Universe was around a third of its current age, at which time most of its structure had already formed and evolved. So Earendel is indeed a ground-breaking record.
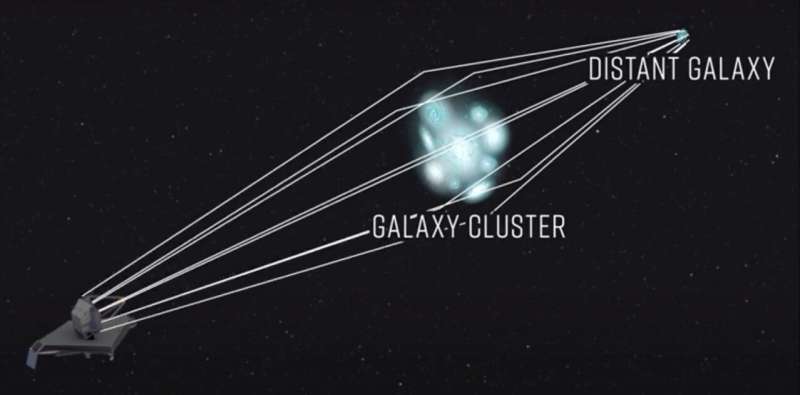
A massive galaxy cluster focuses and magnifies the light from a background galaxy
A target for the James Webb Space Telescope
To measure the brightness of Earendel, the astronomers constructed a physical model of the gravitational lens. The exact nature of the light source depends on their model, but when the astronomers are so certain that the little dot is in fact a single star, it is in part because many different models all give roughly the same answer.
Nevertheless, Earendel could in principle be more than one star, located very close to each other. To test whether this is the case, the team applied for—and were awarded—observing time with the recently launched James Webb Space Telescope.
"With James Webb, we will be able to confirm that Earendel is indeed just one star, and at the same time quantify which type of star it is," says Sune Toft, leader of the Cosmic Dawn Center and professor at the Niels Bohr Institute, who also participated in the study. "Webb will even allow us to measure its chemical composition. Potentially, Earendel could be the first known example of the Universe's earliest generation of stars."
at this distance how do they know its not a galaxy or galaxy cluster for that matter
I thought for sure it was 23 gazillion years old?
Let’s see what the James Webb telescope can see.
50+ solar masses? It’s long gone now. We just have not seen it explode yet.
Been awhile since I did deep dive on astrophysics.
My recollection is that they last estimated the age of the universe - from the ‘big bang’ - at just under 14 billion years, give or take.
So, this area of space should be devoid of any galaxies.
Something’s amiss. Or is the ‘science settled’ on astrophysics, too?
/s
It’s difficult to wrap your mind around that distance.
How is age and distance determined? The answer will surprise you. 28 billion years? They keep telling us it is only 6.5 billion years, then 14 billion , well never mind usefull idiots, we are the projinators of what you must belive, or else!
By examining its spectrum. A star has a very limited spectrum. A galaxy has a spectrum made up of light given off by millions or billions of stars.
Less than the width of one of God’s nose hairs.
“28 billion lightyears away.” Confusing. If the universe is fourteen thousand million years old, then the star that is twenty eight thousand million years away must be on the opposite side of the universe from the earth. Cool photos in the article. Thank you.
I’m confused as well. I was just about to ask how a star could be 28 billion light years away when the universe is supposed to be 15 billion years old. Even in your supposition that we are at opposite ends of the universe, how can the light distance be more than 15 billion years?
To me, the operative words are “most distant star ever seen”. There may not be a last most distant star or galaxy. I believe there is no end to God’s creation. Like snow flakes, they’re all different. They’re all beautiful. So are we to Him.
Very confusing. I get it that Einstein's speed of light only limits how fast things with mass can move thru space, but it doesn't limit how fast space itself can expand, thereby carrying objects having mass along with it for the ride. But it still gives me a headache!
“If the universe is fourteen thousand million years old, then the star that is twenty eight thousand million years away must be on the opposite side of the universe from the earth.”
—
“Why the Light Travel Time Distance should not be used in Press Releases “
https://www.astro.ucla.edu/~wright/Dltt_is_Dumb.html
“If the universe is only 14 billion years old, how can it be 92 billion light years wide?”
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vIJTwYOZrGU
Astrophysics give us explanations about everything from the Big Bang, the start of our universe. They have no explanation of anything about the microsecond before. Thus the dichotomy of God. My bet is on God whom is eternal and eternal is a concept we do not understand thus time is not relevant.
The astrophysicists can not answer this question nor can I
Gives a whole new perspective on “To infinity and beyond!”. Try to imagine what would be seen if you stood on a planet around that “star” and looked in the direction away from earth. Also you really have to wonder just who and what methods are used to make these calculations of distance and age of the universe. Also confirmatory experimental evidence that “black holes” really exist has simply never happened. The point is much of experimental physics are just logical speculation and assumptions.
Yes. I’m pretty confused by the numbers, too, but now I’m going nuts waiting for the Webb Telescope to image it. It’s going to exciting to compare the differences between the two images!
I don’t think the distance is confusing, because they would be looking at a star that is on the other side of the singularity, where the Big Bang happened.
We are presumably 14 billion years out from the singularity and that star would be 14 billion years out from the singularity, but on the other side.
Disclaimer: Opinions posted on Free Republic are those of the individual posters and do not necessarily represent the opinion of Free Republic or its management. All materials posted herein are protected by copyright law and the exemption for fair use of copyrighted works.